Rhizome
Definition
Rhizome is a philosophical concept developed by Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari in their Capitalism and Schizophrenia (1972-1980) project. It is what Deleuze calls an "image of thought," based on the botanical rhizome, that apprehends multiplicities. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhizome_(philosophy)
Rhizomes are not plants. They are not even a type of plant. They are a characteristic in sympodial plant species (comment on [1]).
Biological Definition
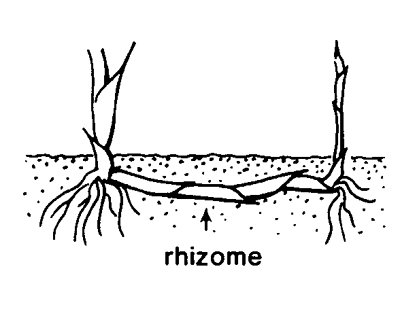
(Science: plant biology) A horizontal underground stem which can send out both shoots and roots, rhizomes sometimes have thickened areas that store starch. A horizontal plant stem with shoots above and roots below serving as a reproductive structure.A type of storage organ in plants which situates itself in a horizontal fashion underground [2].
Discussion
"As long as the plant is connected, all the roots, the roots that dig down everywhere, can share nutrients. They share their life, their energy, their fuel. The rhizome “grows between and among things.” (ATP, 19). It doesn’t need fixed roots. It can send roots down anywhere, and create life, new life" [3].
Highlights
The blog Schizophrenic Summer had a nice set of crucial quotes from Deleuze and Guattari's A Thousand Plateaus, broken into categories:
Rhizome VS. Tree:
“Any point of a rhizome can be connected to anything other, and must be. This is very different from the tree or root, which plots a point, fixes an order” (7). “A rhizome may be broken, shattered at any given spot, but it will start up again on one of its old lines, or on new lines” (9). “Perhaps one of the most important characteristics of the rhizome is that it always has multiple entryways” (12). “Thought is not arborescent … Many people have a tree growing in their heads, but the brain itself is much more a grass than a tree” (15). “Arborescent systems are hierarchical systems with centers of signifiance and subjectification, central automata like organized memories. In corresponding models, an element only receives information from a higher unit, and only receives a subjective affection along preestablished paths” (16). “Such is the principle of roots-trees, or their outcome: the radicle solution, the structure of Power” (17) “The tree is filiation, but the rhizome is alliance, uniquely alliance. The tree imposes the verb ‘to be,’ but the fabric of the rhizome is the conjunction, ‘and … and … and …’ This conjunction carries enough force to shake and uproot the verb ‘to be’” (25).
Unlike a tree …
A rhizome’s “traits are not necessarily linked to traits of the same nature; it brings into play very different regimes of signs, and even nonsign states.” “It is composed not of units but of dimensions, or rather directions in motion. It has neither beginning nor end, but always a middle.” “Unlike a structure, which is defined by a set of points and positions, with binary relations between the points and biunivocal relationships between the positions, the rhizome is made only of lines.” “The rhizome is not the object of reproduction: neither external reproduction as image-tree nor internal reproduction as tree-structure.” “The rhizome is acentered, non-hierarchical, nonsignifying system without a General and without an organizing memory or central automaton, defined solely by a circulation of states.”
Methodologically Speaking:
“A method of the rhizome type, on the contrary, can analyze language only by decentering it onto other registers” (8). “Transversal communications between different lines scramble the genealogical trees. Always look for the molecular, or even submolecular, particle with which we are allied … The rhizome is the anti-genealogy” (11). “[E]stablish a logic of the AND, overthrow ontology, do away with foundations, nullify endings and beginnings” (24).
Unity:
“Multiplicities are rhizomatic … There is no unity to serve as a pivot in the object, or to divide the subject … Puppet strings, as a rhizome or multiplicity, are tied not to the supposed will of an artist or puppeteer but to a multiplicity of nerve fibers” (8). “Unity always operates in an empty dimension supplementary to that of the system considered (overcoding). The point is that a rhizome or multiplicity never allows itself to be overcoded” (9).
Collectives / Assemblages:
“An assemblage is precisely this increase in the dimensions of a multiplicity that necessarily changes in nature as it expands its connections. There are not points or positions in a rhizome, such as those found in a structure, tree, or root. There are only lines” (8). “To these centered systems [are contrasted] finite networks of automata in which communication runs from any neighbor to any other, the stems or channels do not preexist, and all individuals are interchangeable, defined only by their state at a given moment—such that the local operations are coordinated and the final, global result synchronized without a central agency” (17).
Problems with forcing a tree/root metaphor on things that don’t function that way:
“[They] do not reach the abstract machine that connects a language to the semantic and pragmatic contents of statements, to collective assemblages of enunciation, to a whole micropolitics of the social field” (7). {Note to self: explore what “collective assemblages of enunciation” means from a rhetoric of social movements standpoint} “The State’s pretension to be a world order, and to root man” (24).